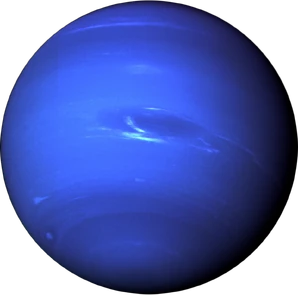
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun in the Solar System. In the Solar System, it is the fourth-largest planet by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet.
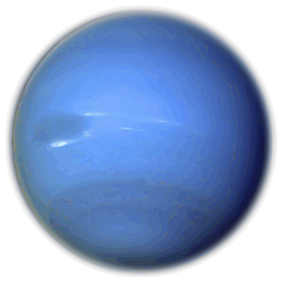
Neptune is 17 times the mass of Earth, slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus. Neptune is denser and physically smaller than Uranus because its greater mass causes more gravitational compression of its atmosphere. Neptune orbits the Sun once every 164.8 years at an average distance of 30.1km. It is named after the Roman god of the sea and has the astronomical symbol ♆, a stylised version of the god Neptune's trident.
Neptune is not visible to the unaided eye and is the only planet in the Solar System found by mathematical prediction rather than by empirical observation. Unexpected changes in the orbit of Uranus led Alexis Bouvard to deduce that its orbit was subject to gravitational perturbation by an unknown planet. The position of Neptune was subsequently calculated from Bouvard's observations, independently, by John Couch Adams and Urbain Le Verrier after his death.

Neptune was subsequently observed with a telescope on 23 September 1846[1] by Johann Galle within a degree of the position predicted by Le Verrier. Its largest moon, Triton, was discovered shortly thereafter, though none of the planet's remaining known 13 moons were located telescopically until the 20th century. The planet's distance from Earth gives it a very small apparent size, making it challenging to study with Earth-based telescopes.
Neptune was visited by Voyager 2, when it flew by the planet on 25 August 1989.[2] The advent of the Hubble Space Telescope and large ground-based telescopes with adaptive optics has recently allowed for additional detailed observations from afar.
Like Jupiter and Saturn, Neptune's atmosphere is composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, along with traces of hydrocarbons and possibly nitrogen, though it contains a higher proportion of "ices" such as water, ammonia and methane. However, similar to Uranus, its interior is primarily composed of ices and rock;[3] Uranus and Neptune are normally considered "ice giants" to emphasise this distinction.[4] Traces of methane in the outermost regions in part account for the planet's blue appearance.[5]

In contrast to the hazy, relatively featureless atmosphere of Uranus, Neptune's atmosphere has active and visible weather patterns. For example, at the time of the Voyager 2 flyby in 1989, the planet's southern hemisphere had a Great Dark Spot comparable to the Great Red Spot on Jupiter. These weather patterns are driven by the strongest sustained winds of any planet in the Solar System, with recorded wind speeds as high as Template:Convert.[6] Because of its great distance from the Sun, Neptune's outer atmosphere is one of the coldest places in the Solar System.[7][8] Neptune has a faint and fragmented ring system (labelled "arcs"), which was discovered in 1984, then later confirmed by Voyager 2.[9]
References[]
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedHamilton - ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Citation/CS1/Configuration' not found.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedPodolak Weizman et al. 1995 - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedLunine 1993 - ↑ Munsell, Kirk (13 November 2007). Neptune overview. NASA. Archived from the original on 3 March 2008. Retrieved on 20 February 2008.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Citation/CS1/Configuration' not found.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedhubbard - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namednettelmann - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedring1
| Solar System |
|---|
| Mercury • Venus • Earth • Moon • Mars • Jupiter • Saturn • Uranus • Neptune • Pluto • Nibiru (A.K.A. Planet X) |